So you’ve decided to take the plunge and start your own SaaS company.
That’s great news! SaaS business is one of the fastest-growing industries on the planet and your chance to change the world forever.
This article will provide you with the steps toward SaaS stardom, as well as actionable tips and advice from industry experts that will help you avoid roadblocks and grow at breakneck speed.
Let’s dive right in and see where your adventure begins.
Focus On Developing a Solution to a Real-World Problem
The one thing that unites the diverse world of software solutions is that each one of them solves a real-world problem.
To follow in the steps of giants like Dropbox, Spotify, and HubSpot, you need to come up with a software idea that meets a real need on the market.
Conversely, building a product that no one really needs will almost certainly spell out doom.
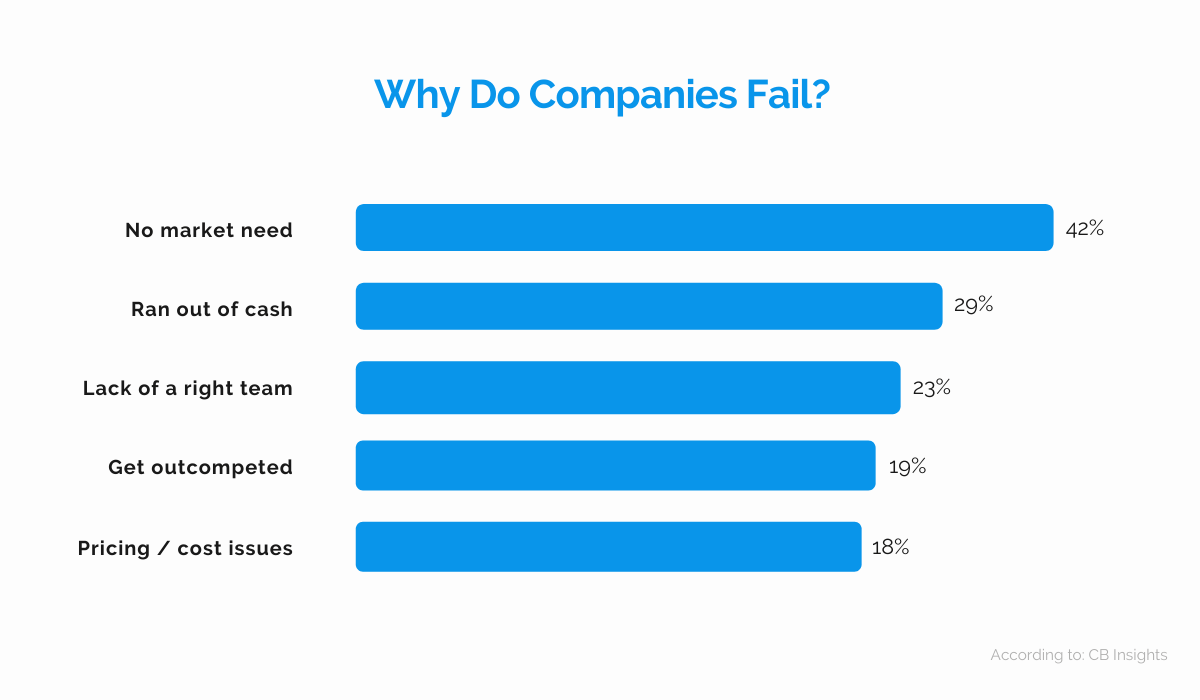
The image above is the result of a “post-mortem” study of failed startups conducted by CB Insights in 2019. It determined that almost half of startups fail because they don’t respond to a market need. In other words, they go under because they don’t solve a real-life problem.
Therefore, your first step to building a successful SaaS business from the ground up isn’t coming up with an idea. It’s discovering a problem. Once you’ve done that, you can concentrate on finding a solution.
The first part of this equation is called finding a product-solution fit. It involves researching the market for a specific need that isn’t being met adequately.
At this junction, you should be asking yourself three questions.
- Who is my audience?
- What problem is my audience having?
- Are there any existing solutions to this problem?
Once you identify a problem shared by a large segment of the audience and determine that the current solutions don’t do it justice, it’s time to develop the game-changing solution that’s going to be the foundation of your SaaS company.
This second act is called finding the product-market fit. This step is all about validating your solution before you introduce it to the market.
Your perfect product needs to:
- Solve the problem adequately
- Solve it better than the competition
- Solve the problem for a reasonable price the audience is willing to pay
The image below explains this concept in visual terms.
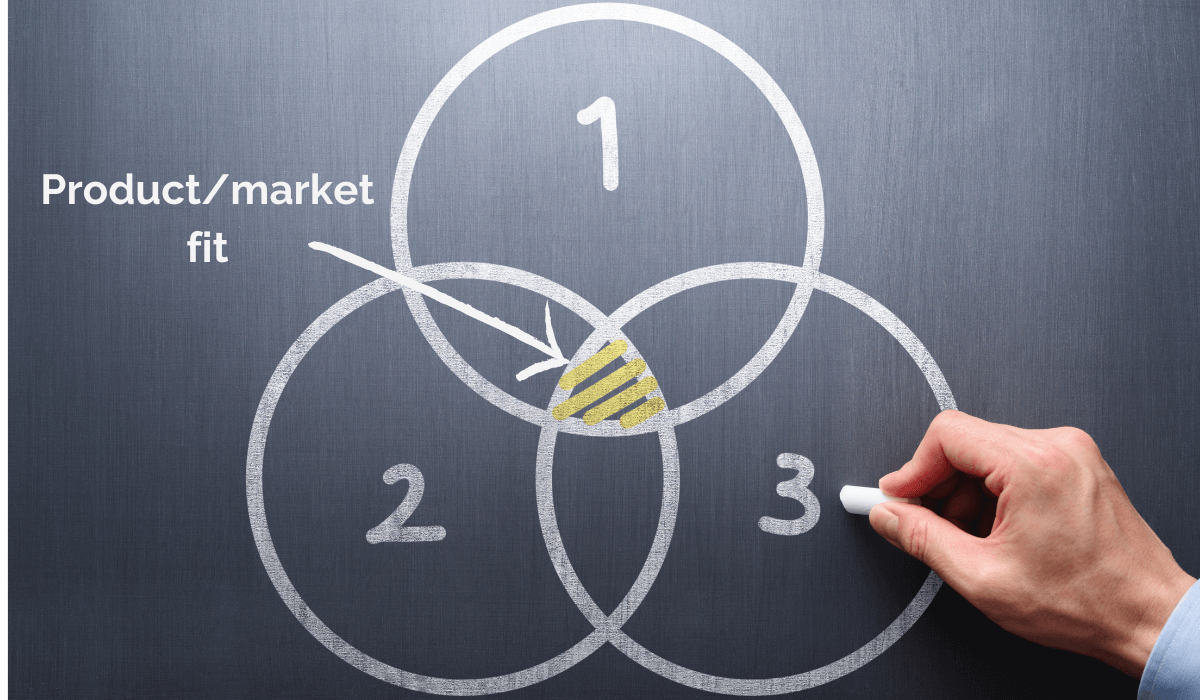

A perfect product-market fit is an intersection where your product hooks the interest of a targeted market segment by offering a solution to a shared problem for a price that suits the people who share this problem.
In conclusion, building a SaaS business doesn’t start with an idea. It starts with a problem. Begin your journey by identifying a problem shared by a large segment of the market, and then go on to developing a software solution that solves it better than any other.
Conduct Market Research
Good market research is the basis of every successful startup. It’s a way to find out which ideas have a future in the competitive world of SaaS.
Doing market research is critical because it prevents you from creating a product that the consumer has little need for. Think of this step as a guiding light toward success.
Market research starts after you’ve successfully identified a problem and imagined a potential solution. It’s an integral part of finding the perfect product-market fit.
There are actually two aspects to consider: competitive analysis and audience research.
Competitive analysis is focused on your competition. It means taking a long, hard look at the market and examining the solutions that already exist.
The trick isn’t to find a market that no company has tapped yet. Rather, a competitive analysis can show you where others have failed so you can learn from their mistakes to create a better product.
A great way to do that is to build a template that showcases different aspects of your company and compares it to your main competitors, like in the example below.
Source: Slide Bazaar
Audience research represents the other side of the same coin. It means reaching out and talking to your future customers to find out their pain points, what the perfect software solution would entail, and what it should cost.
Researching your audience is incredibly rewarding when it’s done face-to-face. However, this qualitative approach should be supported with quantitative methods, such as a strong survey.
Online surveys allow you to reach a wide audience and generate a lot of data. Tools like SurveyMonkey can help you create enjoyable surveys you can send to your mailing lists or share on social media to gather the answers to all of your questions.
Source: SurveyMonkey
Once you pick up on the gaps in your competitors’ product and find out exactly what your customers want, you’ll be left with a laser-sharp idea for a product that is sure to catch your audience’s attention.
Your next step is to build a company around your excellent product.
Start With Lean Planning
Back in 2012, 75% of all startups failed. This happened in spite of the fact that they were based on great ideas, responded to a market need, and had adequate financial support.
The problem, it seems, was that they followed the steps of traditional business plans that were ill-adapted to the needs of software companies. So a new approach was developed, and lean planning was born.
Where traditional business plans favored structure and elaborate steps toward success, lean business plans rely on experimentation, pivoting, and customer feedback.
It worked like a charm. SaaS businesses were released from the constraints of traditional business and allowed to evolve and change, making them sturdier and less risky for investment.
The basic principle of lean planning is that it’s a cycle of continuous improvement, instead of a straight line.
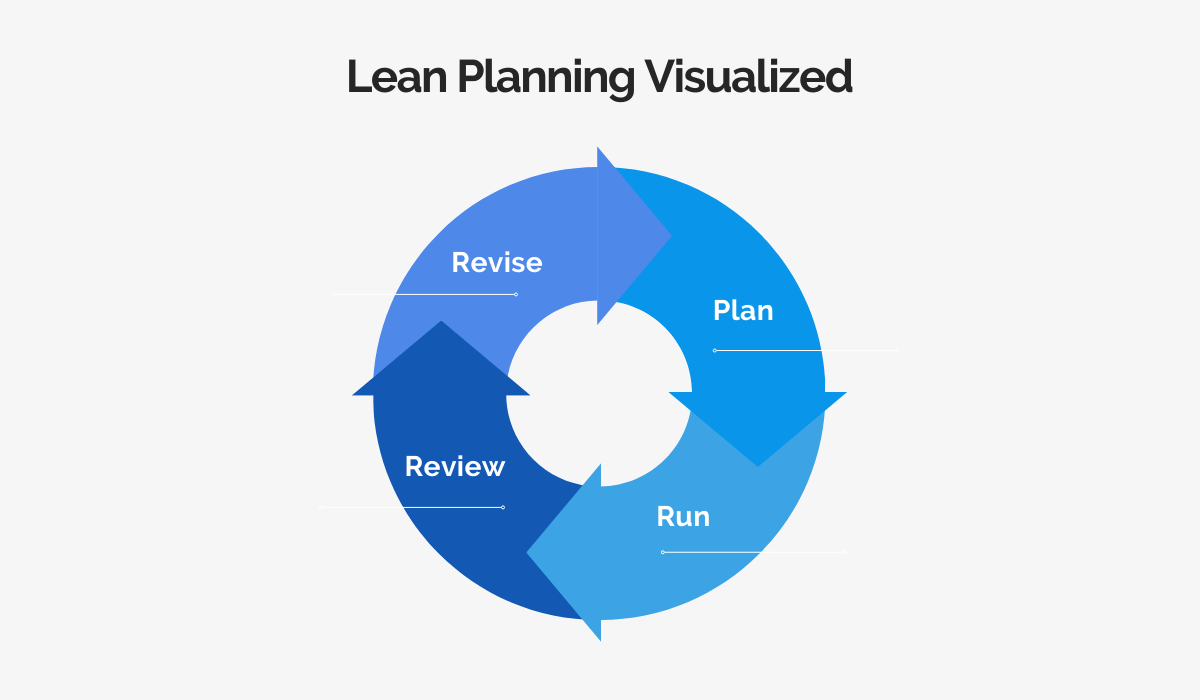
As you can see, lean planning means developing your business on the fly. You should continuously review how your product is doing and what changes need to be made.
Once you have a good idea of how to improve, you can simply revise your plan and incorporate the changes into your product.
After that, the process starts again.
Consequently, you don’t need to slave over a fifty-page business plan. Instead, you can put your time to good use and develop your product.
In fact, your business plan need not be more than a page long. It should just cover the basics, such as:
- Strategy – What your product is and what problems it solves.
- Tactics – How it solves them.
- Schedule – Who’s doing what and when.
- Business model – How you’re making money off the product.
This gives you a starting point from which to put your idea into action.
Once you’re operational, collect feedback and metrics. Make that information available to your whole team so you can work together on finding ways to improve your product.
Gathering and organizing large amounts of data so that the entire team can access and learn from it can be something of a hassle. Consider utilizing software solutions, such as data querying and analytics software which empowers your team to build reports, perform lookups, and get ad hoc answers on the fly.
Remember that your startup’s lean business plan is something that evolves and changes alongside your company. It’s not a document you’ll only look at once and lock away in a drawer forever. Keep it at the forefront of your mind and develop it as you go.
Put Your Idea to the Test With a Prototype
With a fully-formed idea and a company established, you can start developing your product. There are a couple of steps to this, and the first one is building a prototype.
In a nutshell, a prototype is a very early version of your final product. Think of it as more of a presentation than an actual product.
It’s just a sketch of the final result, but it can offer a platform for users to test and provide you with valuable feedback.
In that way, prototypes are another cyclical aspect of the SaaS business model.
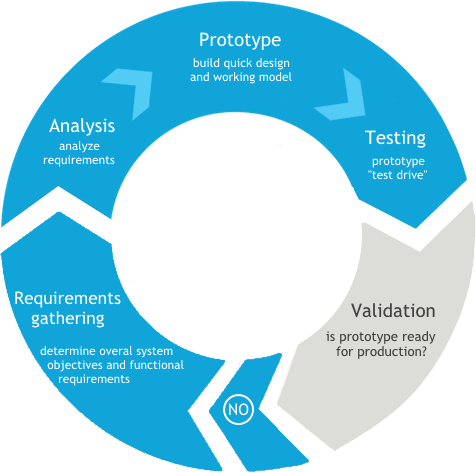
Source: nicenux.com
The graph above shows that the rules that apply are similar to the concept of the lean business plan: test, gather data, improve, repeat.
The benefit here is that you can build something quickly and inexpensively, then share it with an audience to see how they react. Favorable feedback will tell you you’re on the right track. Negative reactions will send you back to the drawing board to improve on your first concept.
Let’s explain this further with an example.
Imagine you’re building a weather app. To present your idea to testers and investors, you would build a prototype that looks real, but doesn’t have interactive features yet.
At this stage, you just want to see if users will respond well to your design and the features you offer.
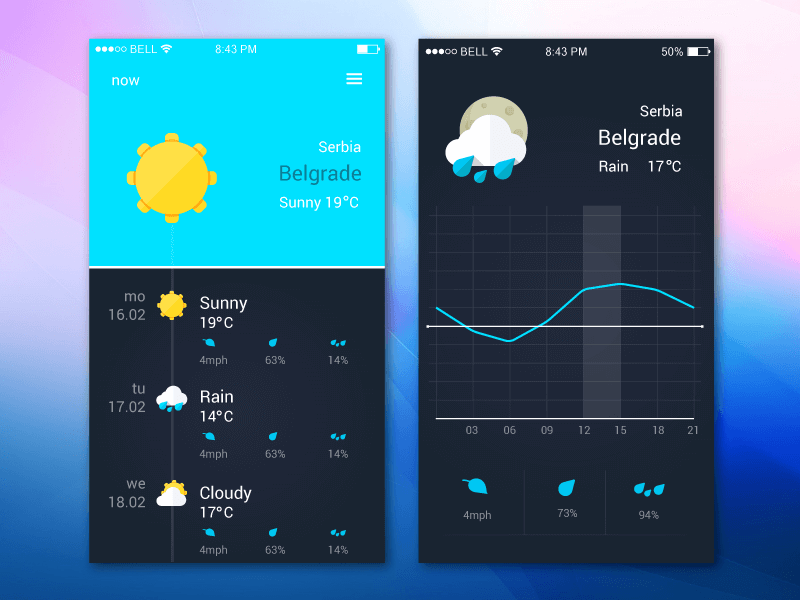
Source: Deviant Art
The image above is how your prototype might look.
You can then share it and ask for feedback on the following:
- Is the design attractive?
- Are there any features missing (e.g., sunrise and sunset times)?
- Are the wind and rain icons easy to recognize and differentiate?
After you’ve collected ample feedback, you can start ways in which the prototype could be improved.
After you’ve perfected the prototype and reached a version your developers, early adopters, and investors are happy with, it’s time to move on to the next stage: developing an MVP.
Create an MVP
With your prototype perfected, you’re halfway there. The next stage is creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a version of your software that finally has usable features but is still mostly used for testing and gathering information.
Like prototypes, MVPs remove a large portion of the risk in SaaS product development by allowing you to develop a basic, inexpensive version of the final product and sharing it with investors, early adopters, your team, and testers to collect feedback.
This is another iteration of the product that will get changed a lot and perfected along the way.
So, what’s different?
Well, since we’ve relied on donut graphs a lot in this article, let’s look at some donuts to understand the difference between prototypes, MVPs, and the final product.

Source: Spark Solutions
As you can see, while the prototype is just an outline, a tool that will help you imagine the final product, the MVP actually gives you something to sink your teeth into, so to speak.
MVPs usually have a working core feature that defines the idea behind the SaaS product.
For example, in 2006, two Swedish entrepreneurs, Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon, launched an MVP that showcased their SaaS idea: music as a subscription service. The MVP was a simple music streaming app.
Source: Altar.io
That’s the MVP they created. Not much to look at, right?
The idea was a great success, so they kept improving on it, topping it off with amazing UX, excellent algorithms, and minimal latency. Today, their final product, the music streaming service Spotify, is worth $50 billion and has over 50 million subscribers.
You can start creating an MVP after you’ve perfected your prototype.
Your MVP should showcase a core feature of your software, so decide which feature you want to build your MVP around. This is the most basic function of the product, your idea made alive. In the above example, the core feature of Spotify’s MVP was streaming music.
Once you’ve selected the core feature, it’s time to map out the user journey. You want to create software that is easy to use and easy to navigate. That means nailing the interface, design, and content to make users fall in love with your product.
Finally, develop the MVP and test, test, test. Collect as much data and feedback as you can and keep tweaking the MVP until it’s perfect, just like you did with the prototype.
The more time you spend improving the MVP, the less you’re going to have to pivot and adapt after the final product launches. With a perfected MVP, you’re finally seeing your product taking shape.
Get the Required Financing
Funding a SaaS product does not come cheap. Luckily, the financial world has recognized the incredible potential of tech startups to generate revenue very quickly after launching.
Consequently, there are multiple sources of funding for you to explore in addition to using your own capital to finance your business.
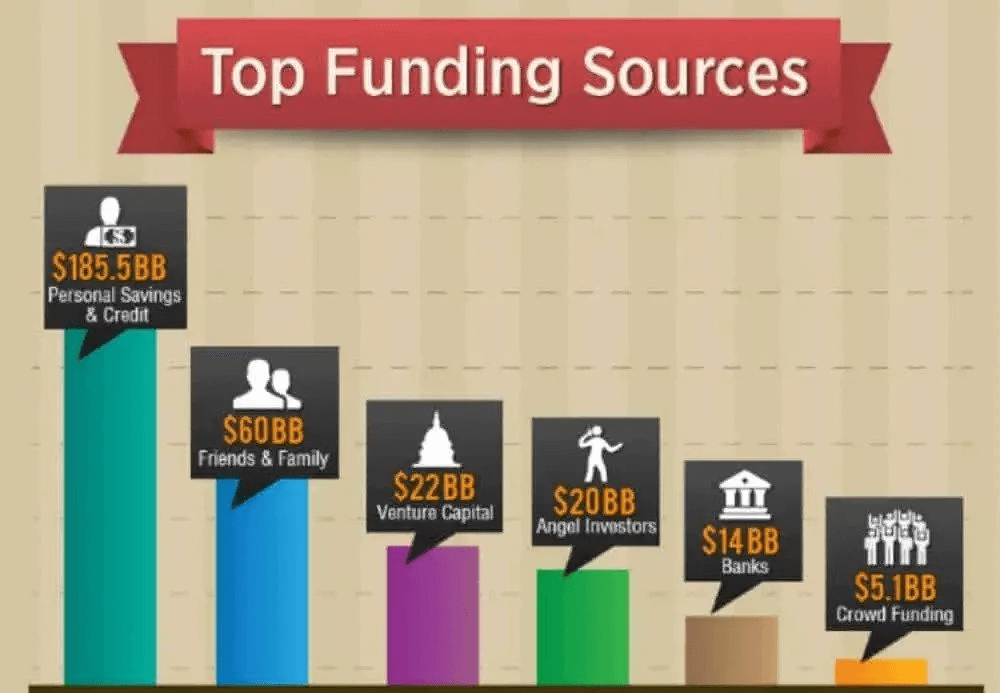
Source: Fundable
Obviously, many entrepreneurs prefer to use their own savings and personal money to fund their projects. Relying on your own capital to fund your business (bootstrapping) means you get to keep total control of your company.
All other sources of capital make your business idea less risky, but they could mean you’ll have to give up some of the control and distribute equity between founders and investors.
Of course, unless you’re starting your SaaS business as a millionaire, financing the entire project by yourself (or within a team of founders) will likely be impossible.
Furthermore, the healthiest startups are the ones who get their funding from more than one source.
Let’s see how different sources of financing connect to your brand new company.
First up, there’s love money. This is financing sourced from friends and family. This is a good source of funds in the very beginning when all you have to show is your talent and integrity.
Looking outside of the family, venture capital and angel investors are the norm.
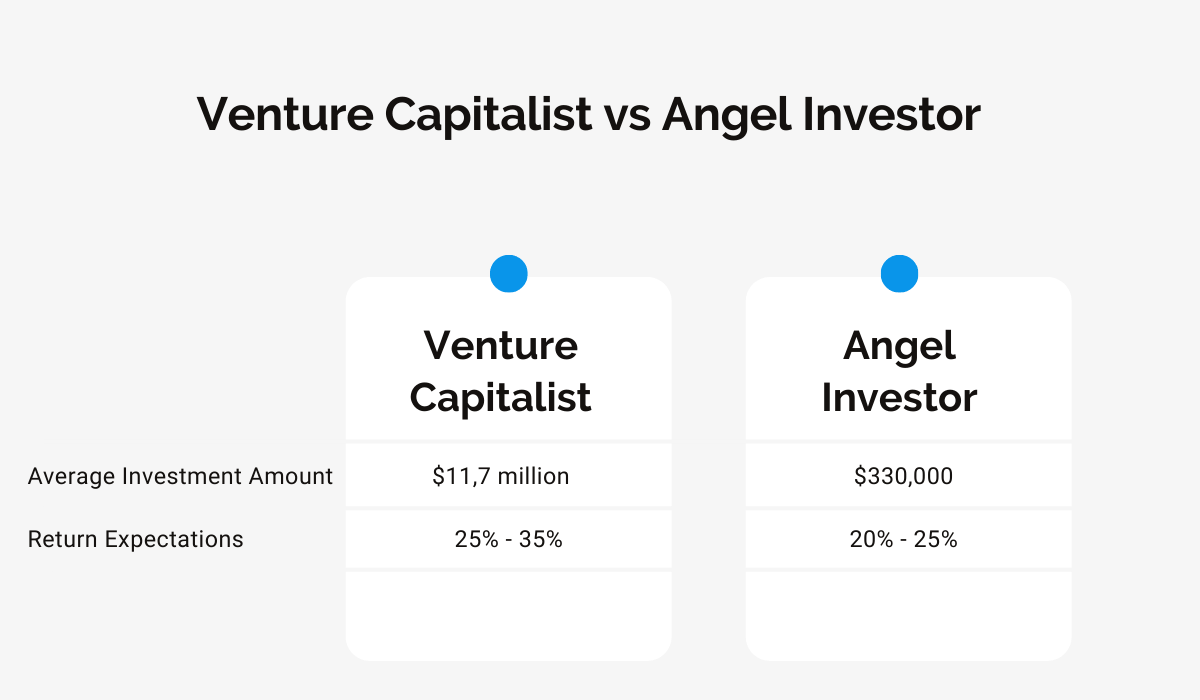
The two sources are similar in that they both represent outside capital from a single entity, but the size of individual investments is very different, as you can see above.
You can expect large financial injections from venture capitalists, so they are best used for large and expensive projects. However, they will expect a hefty percentage of your company and the ability to make large-scale interventions.
On the other hand, angels can invest much smaller amounts of money, while expecting a smaller return on their investment. Furthermore, they usually won’t seek to take control of your company.
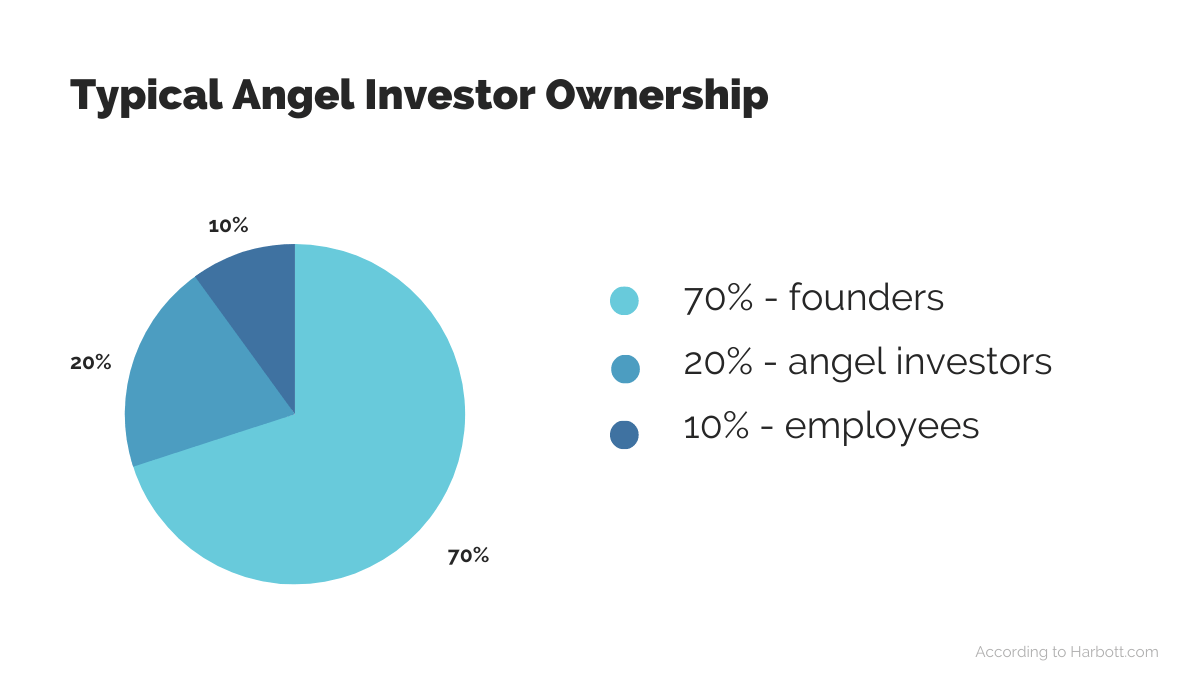
As you can see above, angels usually don’t take up more than 20% of company ownership.
Furthermore, angels are usually (retired) entrepreneurs and technical experts themselves, so their experience and knowledge can be as valuable as their financial investments. Don’t hesitate to involve them in more complex and technical projects.
Smaller financial investments can come from various sources, such as bank loans, crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo, business incubators, and government subsidies.
The takeaway here is that your product deserves quality treatment, and that takes money. There are many funding sources available to you, so choose the ones that will enable you to bring your idea to life and maintain as much control over it as possible.
Build Your Product
When you’re finally ready to build your software, two things are essential: choosing the right technology and finding the right development team.
The building materials used for the construction of your software are the programming languages, frameworks, and tools that make up your tech stack. There are many combinations you can use, and famous SaaS companies each have a formula that works for their needs.
Source: The App Solutions
Airbnb, Netflix, and Dropbox are all famous digital products that offer a reliable service and excellent user experience. However, as you can see, the building blocks that make up each application vary greatly.
You should devote enough effort to find the right stack for your product.
Once you’ve chosen your tech stack, your next step is to find the best developers for the development technology you plan to use. This may prove to be something of a challenge.
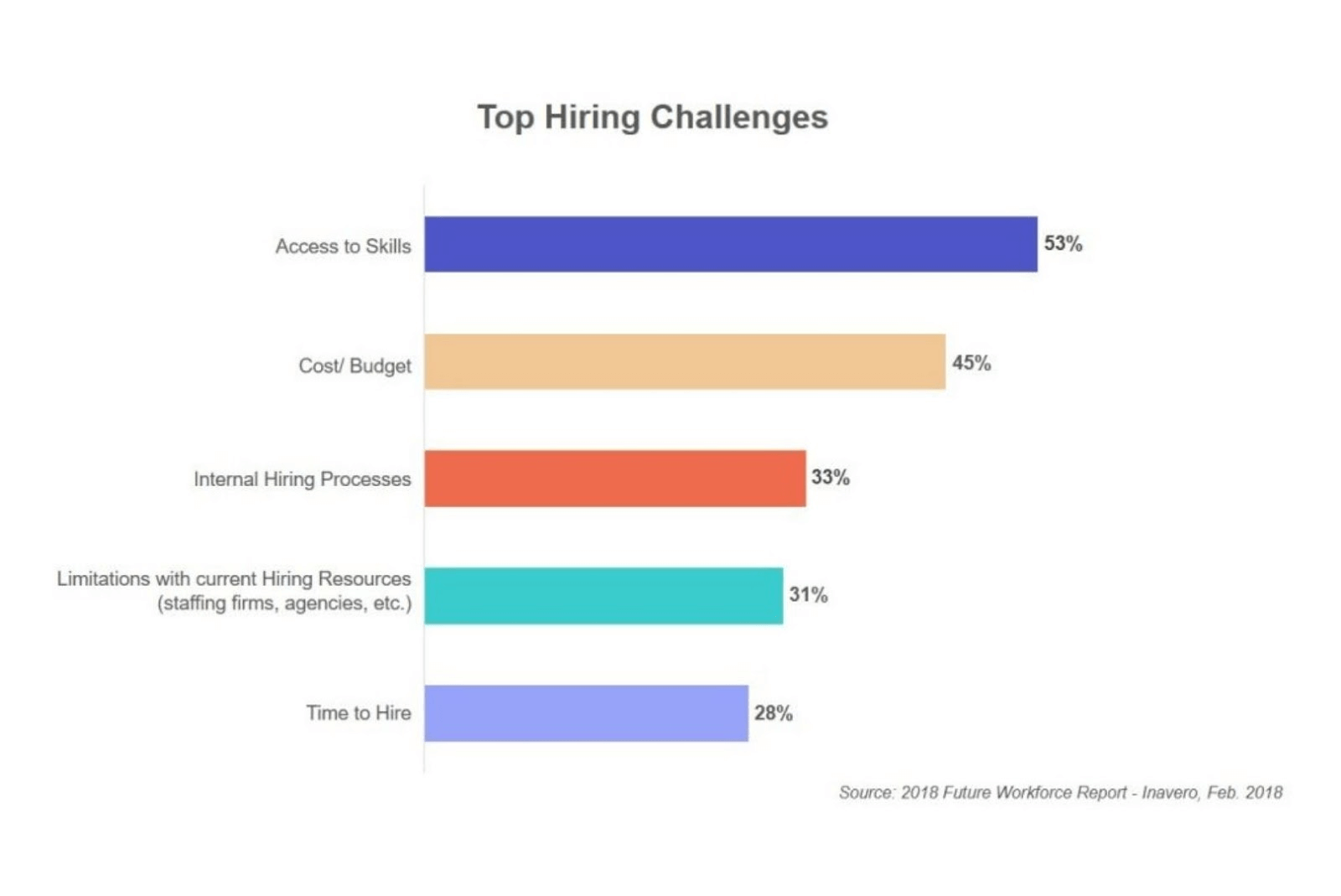
Source: ThirdRockTechkno
As you can see, good software developers are very hard to find these days. Consequently, quality development staff is very expensive.
Therefore, while hiring an in-house team of developers is certainly the best option for any software company, it may not be feasible for new startups.
Luckily, there are alternatives to hiring you’ll find useful.
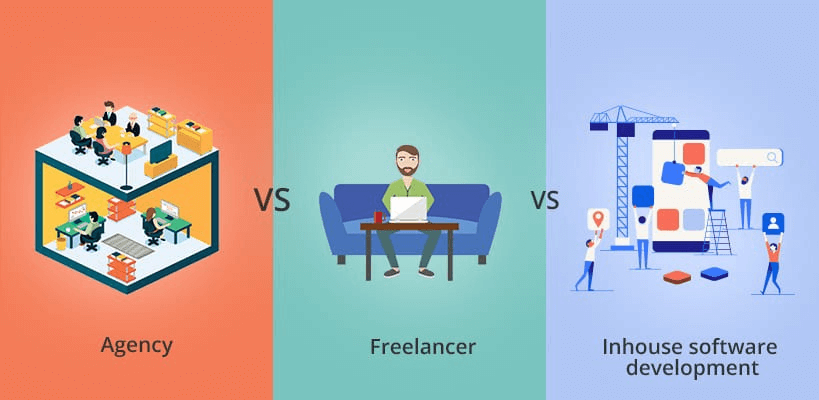 Source: Medium
Source: Medium
The first is using freelance developers. You’re almost certain to find people who can handle every development aspect of your software on platforms like Toptal, Fiverr, or Upwork.
The drawback is that freelancers can abandon you in the middle of the project, and there is no guarantee of quality.
On the other hand, you could outsource the work to a software development agency.
Agencies can carry your project from the initial idea analysis all the way to the final product. They’re reliable and deliver high-quality results, but they can be very expensive.
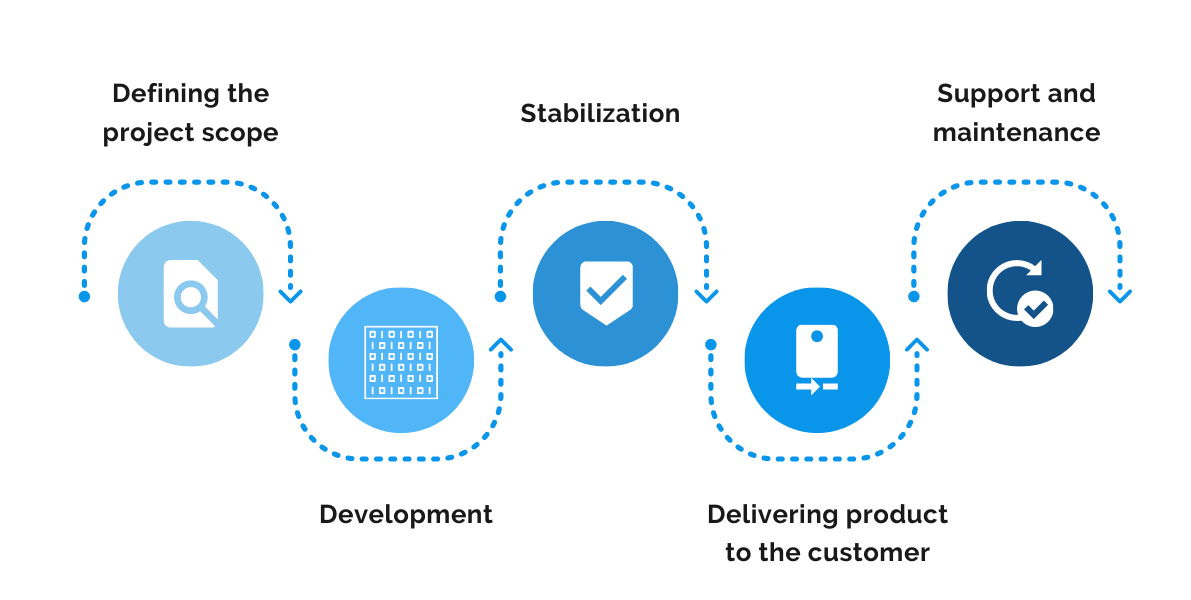
The image above shows you just how much a development agency can do for you.
Finally, if you’re not willing to compromise on quality even though you’re on a tight budget, you could try to find a technical co-founder.
That way, you’re partnering up with an expert who will be dedicated to developing the best possible software solution. As payment, you can give them equity in your company.
Just make sure your co-founder is the perfect fit for your company and someone you get along with, as they will stay with you for a long time.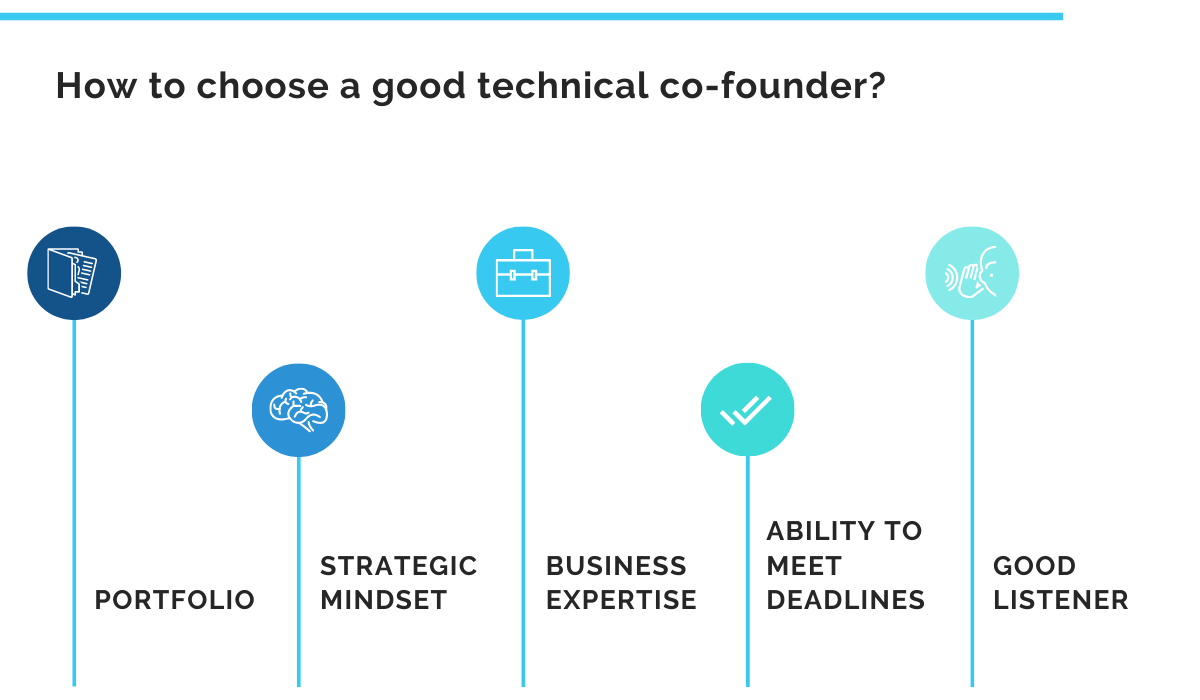
The above image provides some suggestions on the qualities to look for in a technical co-founder.
Remember that building software is much like building a house. You need the right building materials and the right construction crew to guarantee the best results.
Find the Right Pricing Model
With the development process underway, it’s time to set the right price for your software.
The SaaS business model is particularly interesting from the financial perspective because it’s based on the concept of monthly or yearly subscription, instead of a one-time purchase.
Your pricing model should evolve according to the demands of the customers and the features of your product.
As Yoav Shapira, Director Of Engineering at Facebook, says
“The number one tip for pricing strategy is to treat it as an experiment.”
There are multiple pricing strategies for you to try, so don’t be afraid to test until you find the one that best serves your company and your customers.
Here are the pricing models SaaS companies usually adopt.
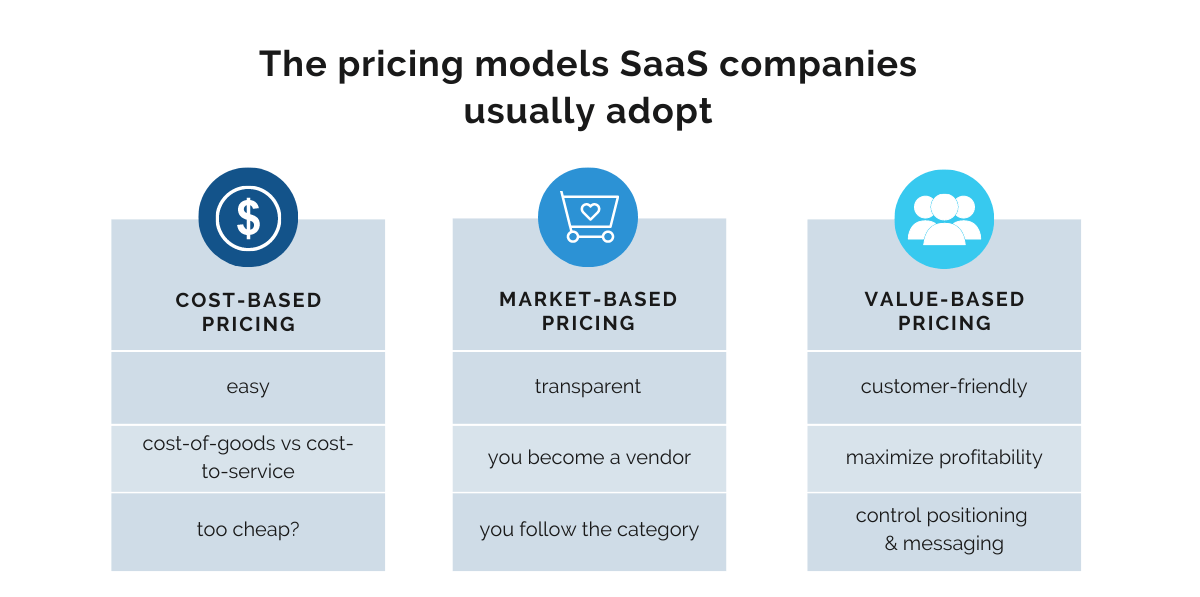
A great starting position for SaaS startups is the cost-based pricing model. This model is really easy to calculate and apply. All you need to do is determine the cost of delivering your service and then add a small mark-up percentage to it.

Source: Online Labels
The above example shows you how you can easily find your profit margin by multiplying your production costs and a desired mark-up percentage.
This is a great way to kick off your business because you have little information to base your pricing on, other than how much your product costs to produce.
As your company grows and produces more value than can be tied to production costs, you may want to try out the market-based model. This is a good transitioning model because it establishes your price according to what the competition is billing for their products.
The challenge here is determining your position in relation to other players on the market.
It may take some trial and error to find the perfect spot so be open to experimentation at this stage and gather a lot of feedback from customers to see how they’re reacting to your prices.
Finally, once you’ve gotten to know your audience, you can move on to value-based pricing, the SaaS business model benchmark.
This pricing model puts the customer in the center and gives them a chance to pay for your software according to their needs, making it very user-friendly.
To apply this model effectively, you should segment your audience according to their level of engagement and the features they use, and then create multiple plans for your customers to select from.
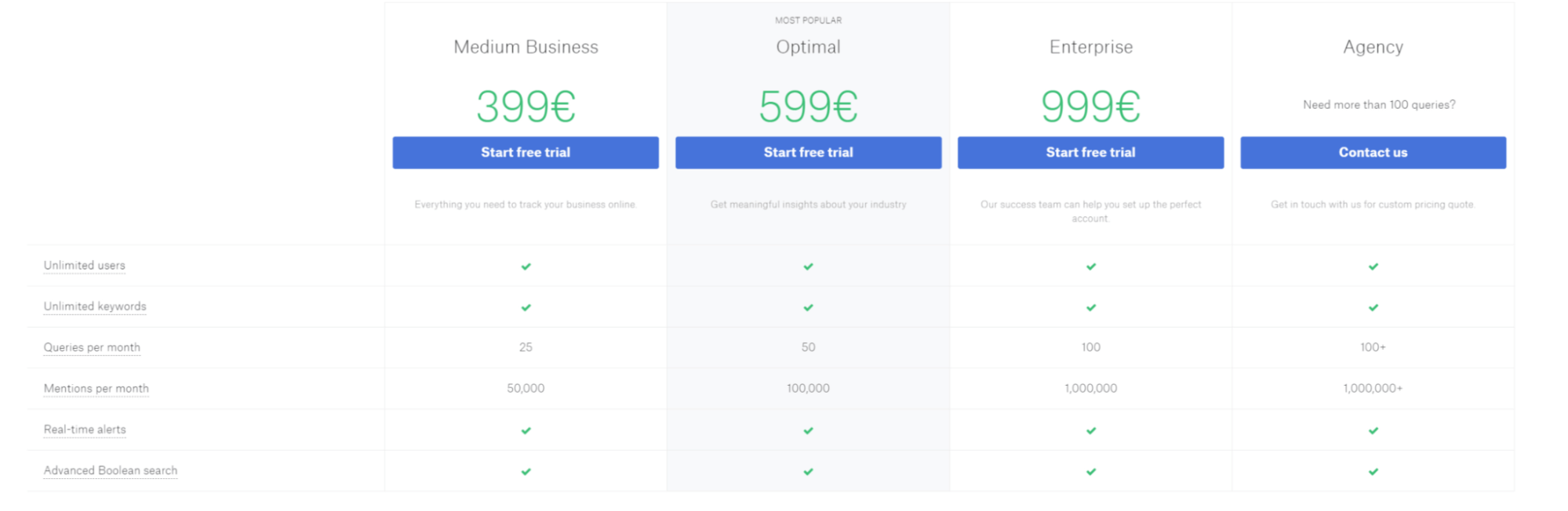
Source: Media Toolkit
For example, the PR tracking software Media Toolkit offers different plans to track online mentions of companies according to company size and media presence.
In conclusion, your SaaS company will evolve and improve its products as it grows. The pricing you offer should be equally flexible while remaining fair for both your business and your customers.
Focus On Building a Brand for Your SaaS Startup
Your customers expect you to tell them a story about why your product is unique, better than any other, and the perfect solution to their problem.
Telling your story is what branding is all about. Without it, you’re invisible to the eye of your audience and your company will fade into oblivion.
Let’s support this with an example.
Have you ever heard of the backlink tracing software called BackRub? It was a revolutionary piece of software back in the ’90s. It crawled the web to discover which web pages generated the most backlinks and therefore could be considered authoritative on a certain subject.

Source: Softpedia
No?
Well, maybe you’ll recognize it after you see how it was rebranded as a search engine in 1998.

Source: HubSpot
Ring any bells?
As you can see, it’s the branding that sticks out in our minds and not the product.
Now that we’ve imparted the importance of branding let’s cover the bases of creating a strong brand that will attract customers like a magnet.
It all begins with an eye-catching design. Think of design as your storefront. It’s what makes people stop in their tracks and take a closer look.
Comprehensive brand design covers everything from your company logo, your website, marketing materials, and your software interface. Design truly is everywhere.
That’s why design should be your top investment priority when building a brand.
If your budget permits it, it’s a good idea to hire an in-house brand designer who will create the initial design of everything you need and then develop that design as your company grows.

Source: Unlock IQ
The image above shows you just how comprehensive brand design can be.
Equally important is the copywriting that tells the story of your brand.
It begins with a name. Names like Google, Netflix, Zoom, and Skype are strong, unique, simple, easy to pronounce, and memorable. They are powerful enough to make us use them as common nouns and verbs in our everyday lives.
Copywriting is also the language you use to speak to your prospects and customers. You’re creating complex software with many technical aspects, but that doesn’t really interest your customers.
What they want is value. To communicate value at every opportunity, use language that’s easy to understand and resonates with human emotion.
Source: Hotjar
Notice how effectively BaseCamp communicates the value of their service. They use four words and a picture, but the story told is familiar to all of us.
Finally, remember that it’s your employees who communicate with your customers. Support them and create a happy work environment. Their satisfaction will spill over to your clients and work like a magnet to attract new customers. When that happens, you’ve turned your employees into brand ambassadors.
Developing your brand is one of the final touches in the process of starting your SaaS company. It’s how people finally notice your product and start to see how it improves their lives. Do your company justice with great branding.
Develop a Killer Marketing Strategy
As we said before, SaaS products are abstract and intangible. Convincing customers they need to integrate your product into their lives is hard work. Having them renew their subscription every month is even harder.
Nevertheless, your marketing strategy converts prospects into paying customers, which makes it essential to the survival and growth of your SaaS company.
Therefore, the goal of your marketing strategy should be user growth. With that in mind, we can divide marketing strategies into two groups. Unscalable and scalable marketing strategies.
Unscalable strategies are the ones that will require a lot of effort on your part and won’t yield high results in terms of user growth.
Nevertheless, these are the starting point of any SaaS startup because they present a low risk and don’t require you to have everything figured out yet.
Some unscalable marketing strategies include:
- Getting your friends and relatives to subscribe to your product
- Writing guest blog posts to link back to your software
- Engaging with potential customers on social media
- Giveaways and trial periods for using your product
- Getting covered by niche media
Once you’ve perfected your product and have a high level of confidence that it’s the best solution out there, you can evolve to scalable marketing strategies.
In this context, scalable means being able to generate massive growth with minimal effort. They also require resources other than effort, such as large financial investments.
These strategies are high-risk, high-reward. If your product isn’t established or if it’s still searching for product-market fit, these methods will yield zero results.
On the other hand, they can convert millions of prospects into customers if the moment is right.
In fact, one of the top venture capitalists of Silicon Valley, Andrew Chen, calls the moonshots because they represent your chance to reach for the moon.
Let’s look at some examples.
SEO. Achieving a good rank on Google can take years. But once you’re there, your place is pretty much secured and you can expect a massive amount of traffic.
For example, imagine trying to beat Trip Advisor and Booking.com to rank for the keyword “Aruba hotels.”
Paid acquisition allows you to essentially buy customers, which takes minimal effort but large investments to ensure your product stays visible.
Source: Behance
The Google Ads network is a great example of paid acquisition. You pay for ads that attract millions of users who are looking for exactly what you’re selling.
Virality. If your product is good enough, it will spread like wildfire just by word of mouth. Think of social networks like Facebook. Facebook exploded because it was a revolutionary way for people to connect.
Outbound sales can generate massive revenue and customer growth. However, it takes a dedicated team which will eat up much of the revenue they create in salaries.
Clearly, your marketing strategy will develop over time. As your company advances, it will take less and less effort to generate bigger gains.
This will take a lot of effort and investment, so it’s best to start as soon as possible.
Conclusion
SaaS startups have their work cut out for them, there’s no doubt about that.
To make it in the modern dog-eat-dog world of business, they need to develop a unique product that solves a major problem shared by many people.
They also need to find proper financing and come up with a memorable brand and effective marketing strategy that will attract customers.
Hopefully, this article has given you a good place to start and useful information for every stage of your journey.
All that’s left for you is to take a leap of faith and start turning your world-changing idea into reality!